Comparing the error sensitivity of IQM with PTW Octavius 729Azienda Provinciale per i Servizi Sanitari, Trento, Italy
A variety of treatment delivery errors were introduced into 4 clinical H&N VMAT plans.
These plans were applied through the IQM onto a PTW Octavius 729 (local Gamma pass rate: 2%/2mm).
Which of the two systems will be able to detect the errors introduced into the VMAT delivery?
Method:
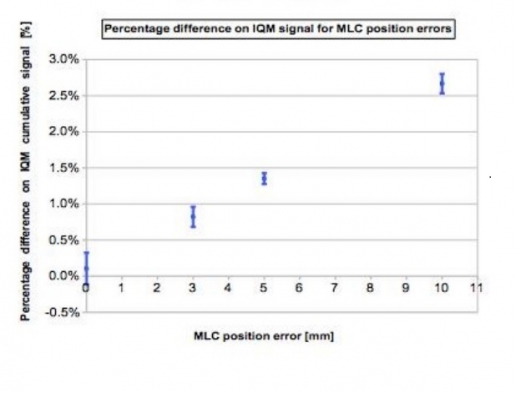
The errors introduced into the 4 H&N VMAT plans were 3, 5 and 10 % errors on total delivered MUs and 3, 5 and 10 mm MLCs shift.
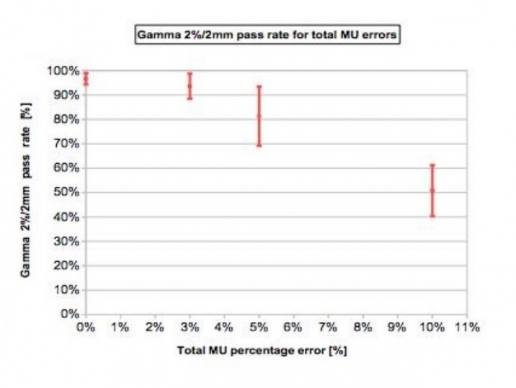
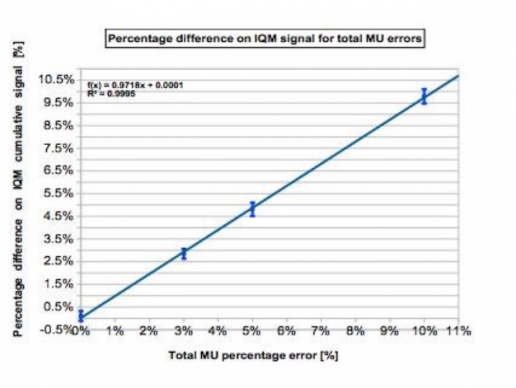
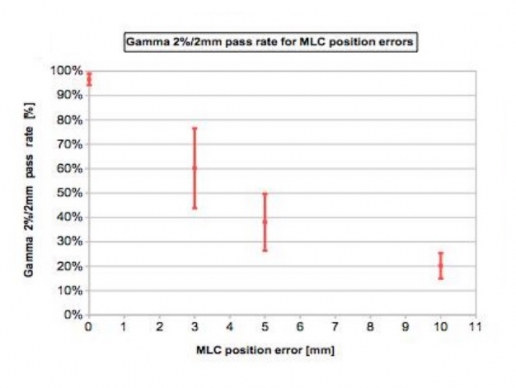
The cumulative IQM checksum value was measured and the percentage difference was calculated with respect to the non-modified plan. At the same time we obtained dose distribution maps through the PTW 2D array inserted in a rotating QA phantom (RT-smartIMRT, dose.point GmbH). The local gamma pass rates (2%/2mm) were compared to the original plan values.
Results:
Both methods detect specifically MLC shift errors, while MUs variations were better identified by IQM.
IQM shows a linear response with dose (R2=0.9995), while gamma analysis seems to have difficulty in identifying 3% and 5% MUs variations
Conclusion:
IQM shows appreciable features in detecting real-time errors and promises considerable time-saving for QA measurements.
Error detection capability compared to Scandidos Delta 4(Radboud UMC, Nijmengen, The Netherlands)
Various IMRT and VMAT clinical beams with induced errors: One segment/control point retraction of leaves by 10, 5 and 2mm and one segment increase of 10, 5 or 2MU
Sensitivity and specificity can be expected to be sufficient for clinical practice, and at least equal to the Scandidos Delta 4
Simulated errors(University of Florence, Italy)
Errors were introduced to an H&N IMRT treatment composed by seven beams (gantry angles = 0°, 40°, 80°, 140°, 220°, 280°, 320°). Errors were introduced by modifying the number of delivered MU (between 1 and 3 ) and by introducing small deviations in leaf positions for each segment of each beam (mimicking an MLC bank error).
I am text block. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
I am text block. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Error detection capability compared to PTW Octavius(Azienda Provinciale per i Servizi Sanitari, Trento, Italy)
The IQM capability in recognizing errors was performed introducing deviations in 4 clinical H&N VMAT plans: 3, 5 and 10% errors on total delivered MUs and 3, 5 and 10mm MLCs shift by means of an homemade Matlab(MathWorks, Natick, MA) script. The cumulative IQM checksum value was measured and the percentage difference was calculated with respect to the non-modified plan. At the same time they obtained dose distribution maps through the PTW 2D array inserted in a rotating QA phantom (RT-smartIMRT, dose.point GmbH). The local gamma pass rates (2%/2mm) were compared to the original plan values.
I am text block. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
I am text block. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Both methods detect specifically MLC shift errors, while MUs variations were better identified by IQM. IQM shows a linear response with dose (R2=0.9995), while gamma analysis seems to have difficulty in identifying 3% and 5% MUs variations.